|
Ground
Ivy
|
| Taken at Barns Ness on 23rd May 2021 using Nikon D500 with Sigma 600 mm zoom lens. |  |
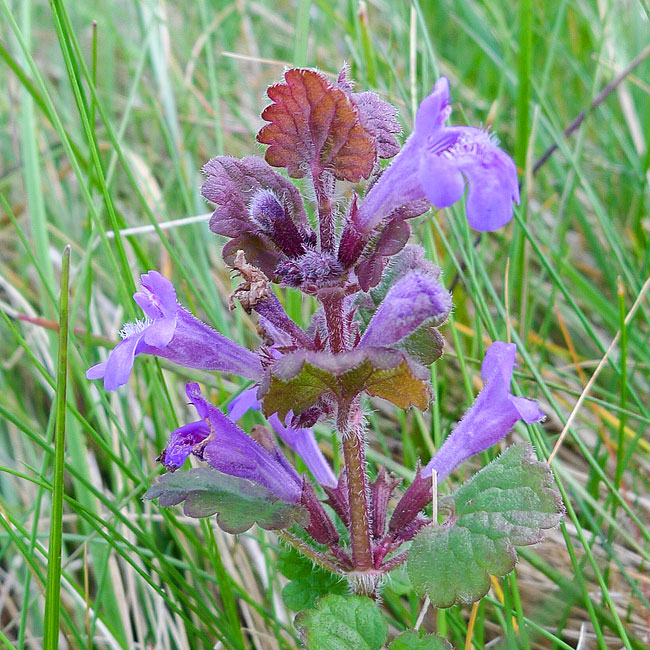

| Taken at Doonfoot on 31st March 2019 using Panasonic Lumix LX5 in macro mode. |  |
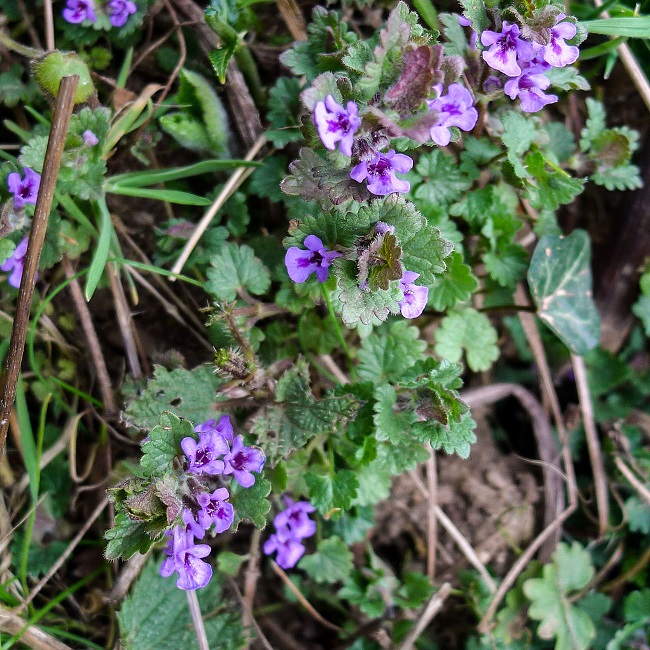
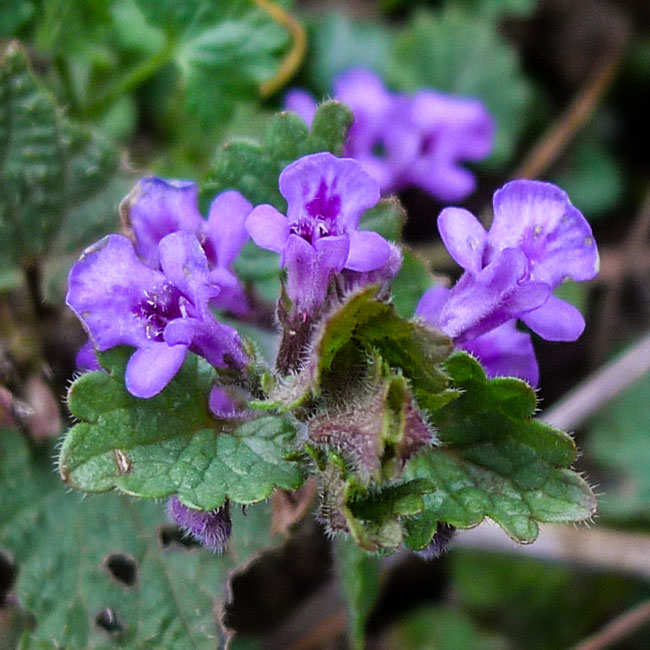


| Taken at Lochwinnoch on 18th April 2019 using Panasonic Lumix LX5 in macro mode. |  |
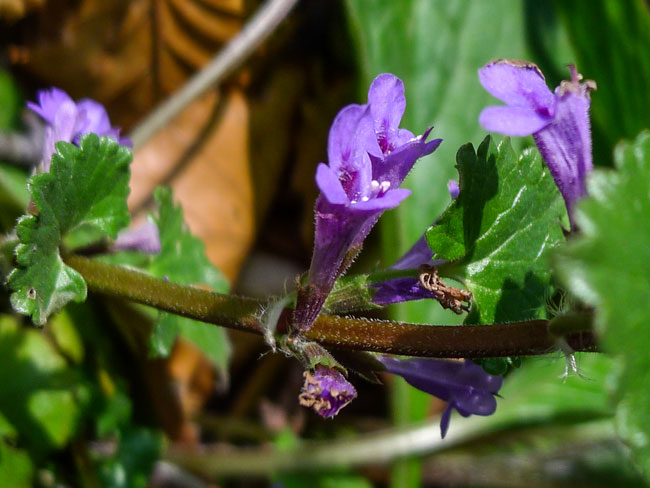

| Ground Ivy. |
| Species: Order: Family: Habit: Local Names: |
Glechoma
hederacea. Lamiales. Lamiaceae. Perennial, evergreen. Gill-over-the-Ground,Creeping Charlie, Alehoof, Tunhoof, Catsfoot, Field Balm, and Run-away-Robin. |
| Habitat: Blooms: Height: Feature: |
Moist shaded areas. Spring. 5 cm up to 50 cm tall depending on environmental conditions. No Relation to Ivy, Hedera helix. This fresh herb can be rinsed and steeped in hot water to create a herbal tea which is rich in vitamin C. It has a distinctive, mildly peppery flavor; it can be cooked as a pot herb, although it is most commonly eaten as a fresh salad green. It was also widely used by the Saxons in brewing beer as flavoring, clarification, and preservative, before the introduction of hops for these purposes; thus the brewing-related names, alehoof, tunhoof, and gill-over-the-ground. It has been used in traditional medicine in Europe for thousands of years . It has been used to treat inflammation of the eyes, tinnitus, bronchitis as well as a diuretic, astringent, tonic and gentle stimulant. Useful in kidney diseases and indigestion. The essential oil of the plant has been used for centuries as a general tonic for colds and coughs, and to relieve congestion of the mucous membranes. In the traditional Austrian medicine the herb has been prescribed for internal application as salad or tea for the treatment of variety of different conditions including disorders associated with the liver and bile, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, kidneys and urinary tract, fever, and flu. However, the safety of Ground Ivy has not been established scientifically and there is sufficient evidence to warrent caution with it's use. |